Cyber Security Course Introduction
Cybersecurity is the technology and process designed to protect networks and devices from attacks, damage, or unauthorized access.
Cybersecurity is essential for a country’s military, hospitals, large corporations, small businesses, and other organizations and individuals since data is now the cornerstone of any organization. If that data is exploited, there are many risks. Now that we have understood cybersecurity, let’s see what the CIA triad is and how it relates to cybersecurity. To gain a deeper understanding and expertise in this field.
CIA Triad
The security of any organization starts with three principles: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. This cyber security for beginners tutorial will teach us about the CIA Triad, the industry standard for computer security since the first mainframes.
- Confidentiality: The principles of confidentiality assert that only authorized parties can access sensitive information and functions. Example: military secrets.
- Integrity: The principles assert that only authorized people and means can alter, add, or remove sensitive information and functions. Example: a user entering incorrect data into the database.
- Availability: The availability principles assert that systems, functions, and data must be available on demand according to agreed-upon parameters based on service levels.
Specialties in Cybersecurity
To pursue your career in cybersecurity, it is essential to know about the areas of specialization in it, and this cyber security for beginners tutorial will help you do just that. There are nine:
- Access control systems and methodology: This protects critical system resources from unauthorized modification.
- Telecommunications and network security: This focuses on communications, protocols, and network services, as well as the potential vulnerabilities associated with each.
- Security management practices: This area effectively deals with catastrophic system failures, natural disasters, and other service interruptions.
- Security architecture and models: This focuses mostly on having security policies and procedures in place. This particular security domain involves policy planning for just about every type of security issue.
- Law, investigation, and ethics: This handles the legal issues associated with computer security.
- Application and system development security: This person covers database security models and implements multilevel security for in-house applications.
- Cryptography: Designed to help you understand how and when to use encryption.
- Computer operations security: This covers everything that happens while your computers are running.
- Physical security: This addresses questions about physical access to your servers and workstations.
Basic Terminologies
1. Network
A network is a connection between two or more computers that communicate. For example:

Fig: Network Connection
2. Internet
Internet connects a computer to any other computer anywhere in the world via dedicated routers and servers.
3. Internet Protocols
Data that is transferred or received cannot follow any path. A set of rules is followed to control the flow of the Internet. These rules are called Internet protocol.
4. IP Address
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is assigned to all devices that connect to a computer network and use the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address looks like this: 168.192.10.3
5. MAC Address
Every device has a unique identification number that connects to the internet. Traditional MAC addresses are 12-digit hexadecimal numbers. MAC address looks like this: D8-FC-93-C5-A5-EO.
6. Domain Name Server(DNS)
Consider DNS as the phonebook of the internet. All the IP addresses and the names of the links are saved in it. For example, you want to go to google.com. You type this on your web application. Then, this name goes to the DNS server, and the DNS server finds the IP address of google.com. Then, the DNS server returns it to your computer with the IP address.
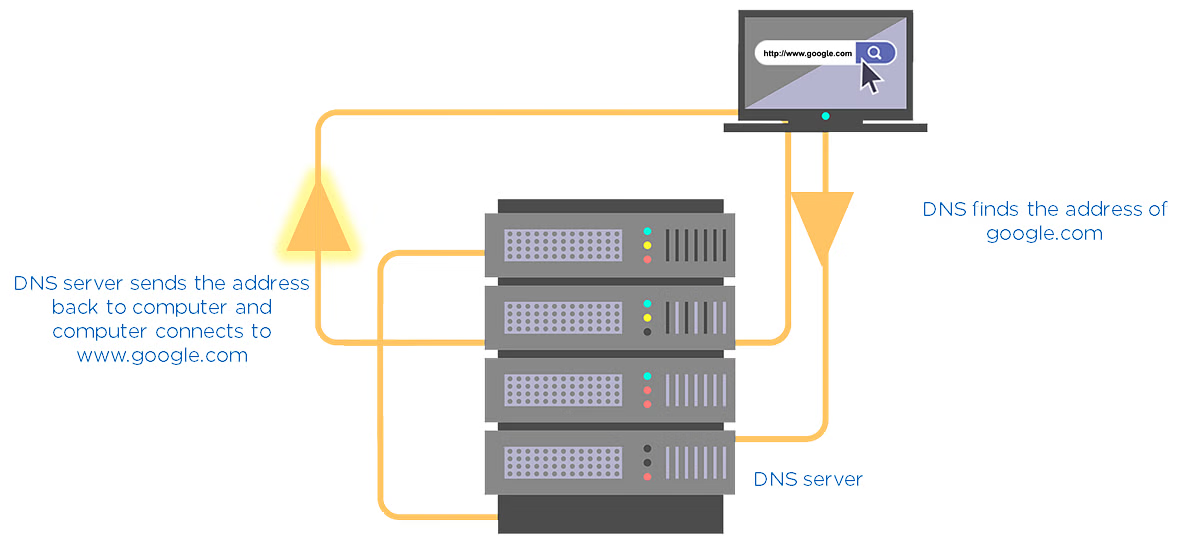
Fig: DNS Server Illustration
Cybersecurity is a popular topic, but do you know why it is essential? We are living in a digital era where data is everything. We must understand that private information is much more vulnerable than ever before. Data breaches and identity theft cases often affect millions of consumers. Two years ago, WannaCry ransomware encrypted millions of computers. All companies and institutions are fighting to protect their data against hackers and cybercriminals, and you can also play a role in it. Cybersecurity is involved not only in organizations but also in personal computers, mobile phones, and tablets.
What is Cybersecurity?
Before we begin this cyber security for beginners tutorial, let’s first understand what cyber security is and its significance. Cybersecurity is the technology and process designed to protect networks and devices from attacks, damage, or unauthorized access.
Cybersecurity is essential for a country’s military, hospitals, large corporations, small businesses, and other organizations and individuals since data is now the cornerstone of any organization. If that data is exploited, there are many risks. Now that we have understood cybersecurity, let’s see what the CIA triad is and how it relates to cybersecurity. To gain a deeper understanding and expertise in this field, one can consider enrolling in the following Cybersecurity Courses.
CIA Triad
The security of any organization starts with three principles: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. This cyber security for beginners tutorial will teach us about the CIA Triad, the industry standard for computer security since the first mainframes.
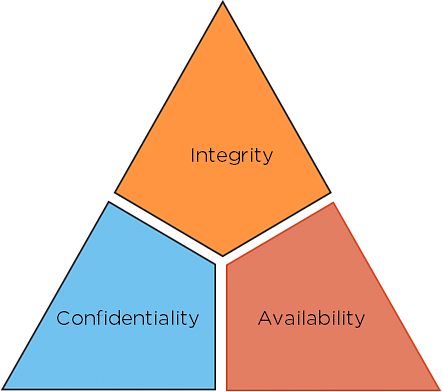
Fig: CIA triad
- Confidentiality: The principles of confidentiality assert that only authorized parties can access sensitive information and functions. Example: military secrets.
- Integrity: The principles assert that only authorized people and means can alter, add, or remove sensitive information and functions. Example: a user entering incorrect data into the database.
- Availability: The availability principles assert that systems, functions, and data must be available on demand according to agreed-upon parameters based on service levels.
Specialties in Cybersecurity
To pursue your career in cybersecurity, it is essential to know about the areas of specialization in it, and this cyber security for beginners tutorial will help you do just that. There are nine:
- Access control systems and methodology: This protects critical system resources from unauthorized modification.
- Telecommunications and network security: This focuses on communications, protocols, and network services, as well as the potential vulnerabilities associated with each.
- Security management practices: This area effectively deals with catastrophic system failures, natural disasters, and other service interruptions.
- Security architecture and models: This focuses mostly on having security policies and procedures in place. This particular security domain involves policy planning for just about every type of security issue.
- Law, investigation, and ethics: This handles the legal issues associated with computer security.
- Application and system development security: This person covers database security models and implements multilevel security for in-house applications.
- Cryptography: Designed to help you understand how and when to use encryption.
- Computer operations security: This covers everything that happens while your computers are running.
- Physical security: This addresses questions about physical access to your servers and workstations.
Basic Terminologies
1. Network
A network is a connection between two or more computers that communicate. For example:

Fig: Network Connection
2. Internet
Internet connects a computer to any other computer anywhere in the world via dedicated routers and servers.
3. Internet Protocols
Data that is transferred or received cannot follow any path. A set of rules is followed to control the flow of the Internet. These rules are called Internet protocol.
4. IP Address
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is assigned to all devices that connect to a computer network and use the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address looks like this: 168.192.10.3
5. MAC Address
Every device has a unique identification number that connects to the internet. Traditional MAC addresses are 12-digit hexadecimal numbers. MAC address looks like this: D8-FC-93-C5-A5-EO.
Did You Know? 🔍
In Q2 2024, organizations experienced an average of 1,636 cyber attacks per week, representing a 30% year-over-year increase.
6. Domain Name Server(DNS)
Consider DNS as the phonebook of the internet. All the IP addresses and the names of the links are saved in it. For example, you want to go to google.com. You type this on your web application. Then, this name goes to the DNS server, and the DNS server finds the IP address of google.com. Then, the DNS server returns it to your computer with the IP address.
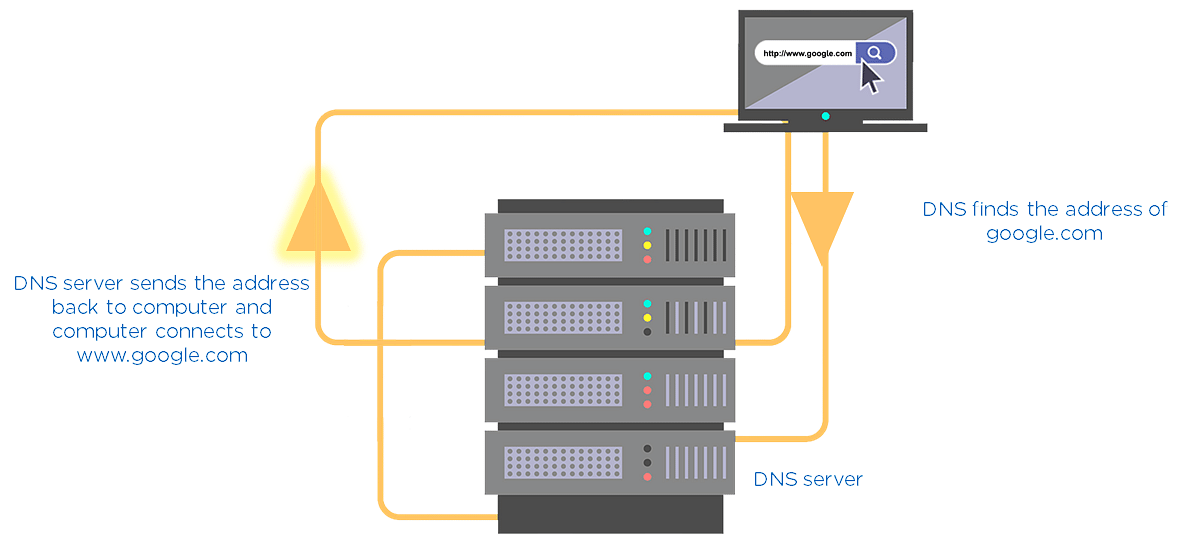
Fig: DNS Server Illustration
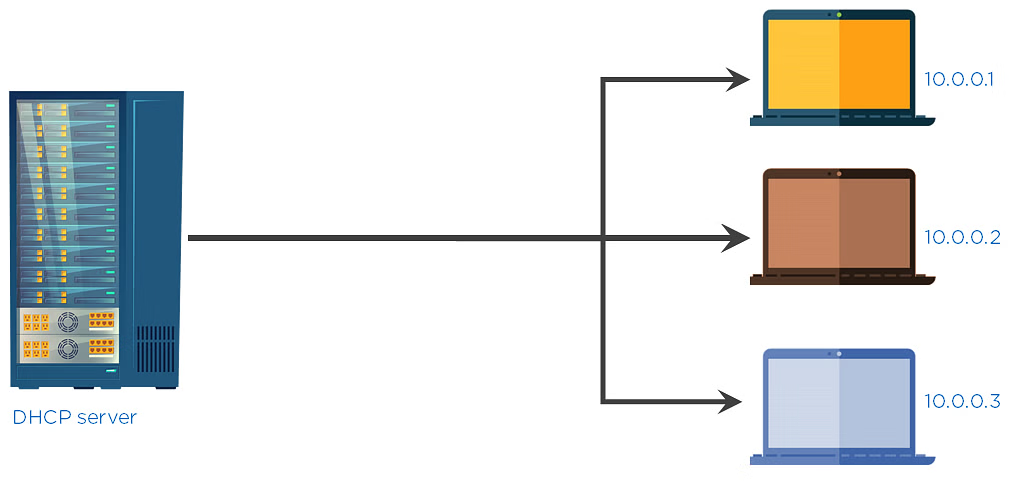
7. DHCP
The dynamic host configuration protocol assigns an IP address to any device that wants to connect to the Internet.
8. Router
This device routes the data that comes to it and then sends it to the destination to ensure that it is on the appropriate path.
9. Bots
Bots are computer programs that control your computer without your knowledge. They automatically send emails, retrieve web pages, and change computer settings.